
Ubuntu installation on AtomMan - step-by-step
1. Preparing the USB Installer Download Balena Etcher. It’s available for Windows, Linux, and macOS. Install it on your system. Download the Ubuntu Desktop ISO: Go to the Ubuntu website and select “Ubuntu 24.04 LTS Desktop.” Click “Download.” You can use a newer version if you want, but for stability, stick with 24.04 unless you specifically need something else. Plug a USB stick (also called a pen drive) into your computer. Open Balena Etcher: Click “Flash from file” and select the Ubuntu ISO you downloaded. Choose your USB stick as the target. Click “Flash” and wait for the process to complete. If you run into any errors, unplug and replug your USB stick and try again. 2. Booting and Installing Ubuntu Insert the USB stick into the AtomMan. Power on the machine and press F2 or Delete to enter the BIOS/Uefi menu. In the boot menu, set the USB stick as the first boot device. Save and exit. The system should now boot into the Ubuntu installer. Select “Try or Install Ubuntu.” 3. Installing Ubuntu Click “Install Ubuntu.” Choose your language and preferences. You can skip connecting to the internet at this stage. When you reach the installation type, choose one of the following: Install Ubuntu alongside Windows Boot Manager - sets up dual boot. Erase disk and install Ubuntu - wipes the drive. Manual/‘Something else’ - for advanced users who want to manually partition their drive (set up efi, swap, and root partitions as needed). Complete the steps for username, password, and time zone. Begin installation and wait until it finishes. When prompted, restart and remove the USB stick. 4. Setting GRUB as the Boot Manager Boot into Ubuntu and open a terminal. Create a mount point for the Windows efi partition: 1 sudo mkdir /mnt/efi-win Identify your efi partition with lsblk. Usually it’s /dev/nvme0n1p1, but check if yours is different. Mount the Windows efi partition: 1 sudo mount /dev/nvme0n1p1 /mnt/efi-win Copy the GRUB efi binary: 1 sudo cp /boot/efi/EFI/ubuntu/grubx64.efi /mnt/efi-win/EFI/ubuntu/ Verify that the file copied successfully. Unmount the partition: 1 sudo umount /mnt/efi-win 5. Updating Windows Boot Manager to Use GRUB Reboot into Windows. Open Command Prompt as Administrator. Enter this command: 1 bcdedit /set {bootmgr} \EFI\ubuntu\grubx64.efi Close Command Prompt and restart your computer. GRUB should now appear when you boot, letting you select Ubuntu or Windows. 6. Troubleshooting and Additional Notes If the touchscreen doesn’t work in AtomMan under Linux, it’s due to missing driver support—there’s no fix for this at the moment. To check your NVIDIA GPU status in Ubuntu: Use nvidia-smi for basic information. Install nvtop (sudo apt install nvtop) for real-time GPU monitoring. In BIOS, ensure “Primary Display” is set to “Auto.” If you have issues, try switching to IGFX. 7. Additional Tips If GRUB doesn’t show up by default, double-check your BIOS boot order. To set the default boot order, you can use tools like boot-repair in Ubuntu. 8. Walkthrough video

Step-by-Step AI Agent Development - From Python to Ansible
Walkthrough video Part 1: Discussion of Steps Creating Documentation in Markdown Each of the main files (index.py, types.dt.py, files from the lib/ directory) should be described in the technical documentation. Below, I present Markdown files with full content. README.md README.md contains general information about the project, its operation, dependencies, and startup instructions. ...

Fundamentals of Ansible playbooks
Introduction Ansible playbooks are written in YAML, a simple and readable format. You don’t need to know programming or coding to start using Ansible. However, there are a few structural rules that you need to follow, and I will explain them step by step. 1. YAML Basics and Indentation Ansible uses YAML syntax for writing playbooks, and YAML is highly dependent on indentation. In YAML, indentation organizes the hierarchy of your tasks or variables, which means you cannot use tabs—only spaces. The most common indentation rule is 2 spaces per level (or sometimes 4 spaces, but consistency is key). ...

Disabling the cups-browsed service on multiple systems using Ansible
The critical vulnerability that was supposed to affect the entire Linux system turned out to be an issue with the CUPS (cups-browsed) printing system. While remote code execution (RCE) without authentication is possible, the flaw only affects systems with the cups-browsed service enabled, which is not common. The vulnerability was published early by security researcher Simone Margaritelli (also known as @evilsocket), who emphasized that it requires specific conditions, such as initiating printing on a spoofed printer. ...
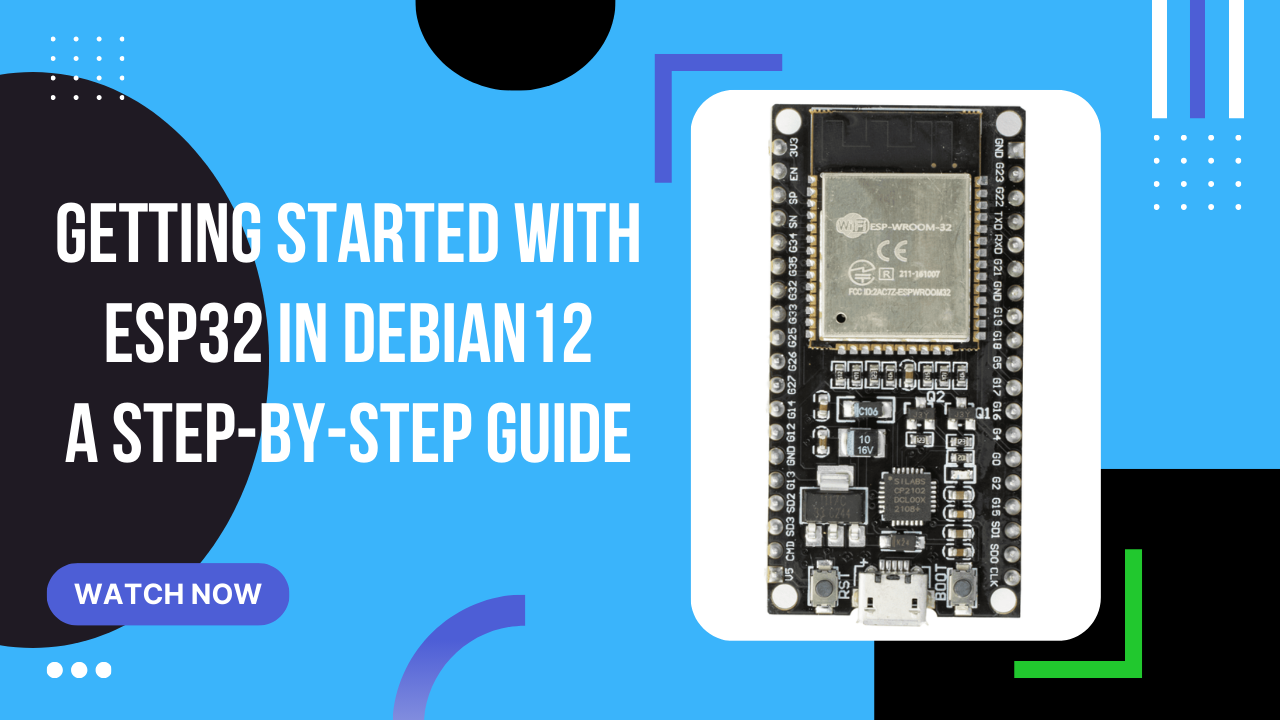
Getting started with ESP32 in Debian 12 - a step-by-step guide
To connect ESP32 to your computer with Linux Debian 12, you will need to follow these steps: USB Cable: You need a USB to micro-USB or USB-C cable, depending on the port type in your ESP32. Drivers: Most modern operating systems automatically recognize ESP32, but you may need to install CP210x USB to UART Bridge VCP drivers. Connection: Connect the USB cable to the ESP32. Connect the other end of the cable to a USB port on your computer. Checking the connection: On Linux, use the command “ls /dev/tty*” in the terminal. You should see a new serial device. Software: For programming ESP32, you can use Arduino IDE or the ESP-IDF platform. Backup Making a copy of the factory ESP32 content is a good idea, especially before introducing your own changes. Here’s how you can do it: ...

Display Twitch Followers on Ulanzi TC001 - A Step-by-Step Tutorial with Node-RED and Home Assistant
This tutorial will guide you through the process of setting up a developer account on Twitch, creating an application, obtaining a client ID and secret, generating a token, and importing a Node-RED flow to interact with the Twitch API to display Twitch followers number on a Ulanzi TC001. Step 1: Setting Up a Developer Account on Twitch Log in to Twitch Go to the Twitch website and log in to your account. Navigate to the Developer Console ...
Integrating OpenBao Password Manager Vault for Enhanced Secret Management in GitLab
Integrating OpenBao Password Manager Vault for Enhanced Secret Management in GitLab Prerequisites Ensure you have root privileges before starting the installation. Automated Installation Script To automate the installation and configuration of OpenBao, use the provided script bao.sh. This script handles the following: Creates a system user and group for OpenBao. Installs Go. Installs necessary dependencies. Installs NVM, Node.js, and Yarn. Clones and builds the OpenBao repository. Configures OpenBao. Generates SSL certificates. Initializes and un seals OpenBao. 9. Creates necessary systemd services. ...

Securing Nexus login data retrieval in Dockerfile via HashiCorp Vault
Introduction To use HashiCorp Vault for storing and retrieving Nexus (NPM) login data during Docker image building, we need to focus on securely storing these credentials in Vault and then retrieving them inside the Docker container during the build process. The key aspect here is using the vault tool in the Docker container to fetch secrets directly during the image build. Steps to follow 1.Storing Nexus (NPM) login data in HashiCorp Vault. 2.Modifying .gitlab-ci.yml to fetch this data inside the Docker container. 3.Modifying Dockerfile to fetch login data from Vault during image build. ...

Effortless HashiCorp Vault unsealing - a step-by-step guide using systemd services
Introduction Vault by HashiCorp requires unsealing after every restart to ensure the security of the secrets it stores. This tutorial will guide you through automating the unseal process using a systemd service on a Linux system. Prerequisites Vault installed and configured on your system Access to unseal keys Basic knowledge of systemd and bash scripting gpg installed for encryption How to install gpg Debian CentOS Fedora Arch OpenSUSE Debian/Ubuntu 1 2 3 sudo apt update sudo apt -y install gnupg gpg --version CentOS/RHEL 1 2 3 sudo yum update sudo yum -y install gnupg gpg --version Fedora 1 2 3 sudo dnf update sudo dnf -y install gnupg gpg --version Arch Linux 1 2 3 sudo pacman -Syu sudo pacman -S gnupg gpg --version OpenSUSE 1 2 3 sudo zypper refresh sudo zypper install gpg2 gpg --version Step 1: Preparation Log in via SSH: Connect to your server as a standard user and switch to root. ...

Secure Secrets Management - Using HashiCorp Vault with GitLab CI/CD
Here is a video tutorial Introduction Below is an integrated tutorial covering the installation of HashiCorp Vault on a separate server and its integration with GitLab Runners. This will ensure secure storage of secrets and their use in GitLab CI/CD pipelines. HashiCorp Vault Documentation Installing HashiCorp Vault on a Separate Server Install Vault: ...